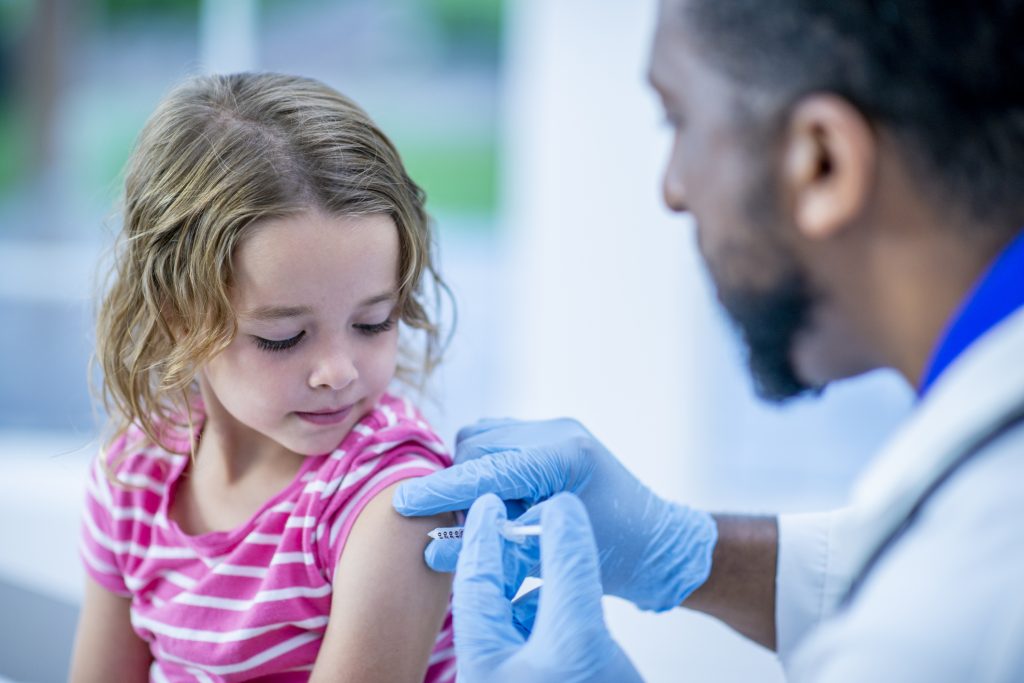

There has been some perplexity and false impressions about immunizations. Yet, immunization is a significant piece of family and general well-being.
Clinics in Sarjapur Road and Bellandur
Immunizations anticipate the spread of infectious, hazardous, and even fatal sicknesses. These incorporate measles, polio, mumps, chicken pox, cough, diphtheria, and HPV.
The primary genuine immunization found was the smallpox vaccine. Smallpox was a deadly illness a century prior. It caused death to millions of individuals around the globe in the twentieth century alone.
The vaccine was given to numerous individuals. The illness was in the long run- eradicated from the earth. It is the main infection which caused complete destruction.
There are presently others near that point. These incorporate polio and mumps. Without the smallpox immunization, a lot more individuals would definitely die. Rather, we don’t should be inoculated for it any longer. This is the thing that antibodies/vaccines can do.
What are immunizations?
An antibody (or inoculation) is an approach to develop your body’s common invulnerability to an infection. This shields you from getting and spreading the sickness.
Immunizations give a development of antibodies before you become ill. That way, you don’t need to experience the side effects of the illness.
For most antibodies, a debilitated type of the illness germ is infused into your body. This is normally finished with a shot in the leg or arm. Your body distinguishes the attacking germs (antigens) and produces antibodies to battle them.
Those antibodies at that point remain in your body for a significant lot of time. As a rule, they remain for an incredible remainder. In the event that you are ever presented to the illness again, your body will ward it off and you will be invulnerable to it.
Be that as it may, it does this without you regularly getting the infection. So, you get the insurance without being sick again.
Clinics in Sarjapur Road and Bellandur
A few sicknesses, similar to strains of cold infections, are genuinely gentle and don’t cause numerous issues.
Be that as it may, a few, similar to smallpox or polio, cause life changing movements and can even bring about death. So, protecting your body from sicknesses is significant.
How does immunity work?
Your body develops a barrier framework to battle outside germs that could make you sick or hurt you. It’s called your immunity framework.
To develop the safe framework, the body must be presented to various germs. At the point when your body is presented to a germ just because, it begins creating antibodies to battle it.
In any case, that requires some serious energy. You typically become ill before your antibodies have developed. In any case, the antibodies remain in your body. So, whenever you’re presented to that germ, the antibodies will assault immediately, and you won’t get the sickness.
Way to improved wellbeing
Everybody needs immunizations. They are prescribed for newborn children, kids, young people, and grown-ups. There are generally acknowledged vaccination plans accessible.
They list what immunizations are required, and at what age they ought to be given. Most are given to youngsters. It is suggested that kids get 14 distinct antibodies by their sixth birthday celebration.
A portion of these arrive in a progression of shots. A few antibodies are consolidated so they can be directed together with less shots.
It accepts that vaccination is basic to anticipating the spread of infectious sicknesses. Antibodies are particularly significant for in danger populaces, for example, youthful youngsters and more seasoned grown-ups. It offers inoculation suggestions, vaccination calendars.
Is there any individual who can’t get immunizations?
There are a few people who can’t or shouldn’t get immunizations. These incorporate newborn children who are excessively youthful (under 2 months) and individuals with certain therapeutic issues.
There are additionally few individuals who don’t react to a specific antibody. Since these individuals can’t be inoculated, it’s significant that every other person gets immunized.
This helps save the “group invulnerability” for by far most of individuals. This implies if a great many people are invulnerable to an infection as a result of inoculations, it will quit spreading.
Clinics in Sarjapur Road and Bellandur
Inoculation shields kids from genuine ailment and complexities of antibody preventable issues which can incorporate removal of an arm or leg, loss of motion of appendages, hearing disorder, spasms, mind harm.
Antibody preventable sicknesses, for example, measles, mumps, and cough are as yet a risk. They keep on contaminating on youngsters, bringing about hospitalizations and will keep on consistently.
Despite the fact that inoculation has prompted a sensational decrease in the quantity, instances of a few irresistible infections, a portion of these ailments are very regular in different nations and are brought to by global explorers. In the event that youngsters are not inoculated, they could without much of a stretch get one of these ailments from an explorer or while voyaging themselves.
Flare-ups of preventable pain or sickness happen when parents choose not to immunize their kids.
Inoculation is sheltered and compelling. All antibodies experience long and cautious audit by researchers, specialists, and the central government to ensure they are protected.
Immunization secures others you care about, including relatives, companions, and grandparents.
Clinics in Sarjapur Road and Bellandur
On the off chance that youngsters aren’t immunized, they can spread illness to other kids who are too youthful to be in any way inoculated or to individuals with debilitated insusceptible frameworks, for example, transplant beneficiaries and individuals with malignancy. This could bring about long haul complexities and even passing for these helpless individuals.
We as a whole have a general wellbeing duty to our networks to secure one another and each other’s youngsters by immunizing our very own relatives.
| Age | Vaccine | Immunization Against |
| Birth | BCG
Hepatitis B – 1st dose |
Tuberculosis
Hepatitis B |
| 1 Month | Hepatitis B – 2nd dose | Hepatitis B |
| 3 Months | DTaP – 1st dose
IPV – 1st dose Hib – 1st dose Pneumococcal Conjugate – 1st dose |
Diphtheria, Pertussis & Tetanus
Poliomyelitis Haemophilus influenza type b vaccine Pneumococcal Disease |
| 4 Months | DTaP – 2nd dose
IPV – 2nd dose Hib – 2nd dose |
Diphtheria, Pertussis & Tetanus
Poliomyelitis Haemophilus influenza type b vaccine |
| 5 Months | Hepatitis B – 3rd dose*
DTaP – 3rd dose IPV – 3rd dose Hib – 3rd dose Pneumococcal Conjugate – 2nd dose |
Hepatitis B
Diphtheria, Pertussis & Tetanus Poliomyelitis Haemophilus influenza type b vaccine Pneumococcal Disease |
| 5-6 months | Hepatitis B – 3rd dose* | Hepatitis B |
| 12 months | MMR – 1st dose
Pneumococcal Conjugate – 1st booster |
Measles, Mumps & Rubella
Pneumococcal Disease |
| 15-18 months | MMR – 2nd dose** | Measles, Mumps & Rubella |
| 18 months | DTaP – 1st booster
IPV – 1st booster Hib – 1st booster MMR – 2nd dose** |
Diphtheria, Pertussis & Tetanus
Poliomyelitis Haemophilus influenza type b vaccine Measles, Mumps & Rubella |
| 10-11 years^ | Tdap – 2nd booster
Oral Polio – 2nd booster |
Tetanus toxoid, reduced diphtheria toxoid and acellular pertussis
Poliomyelitis |
